Query Processing 개요
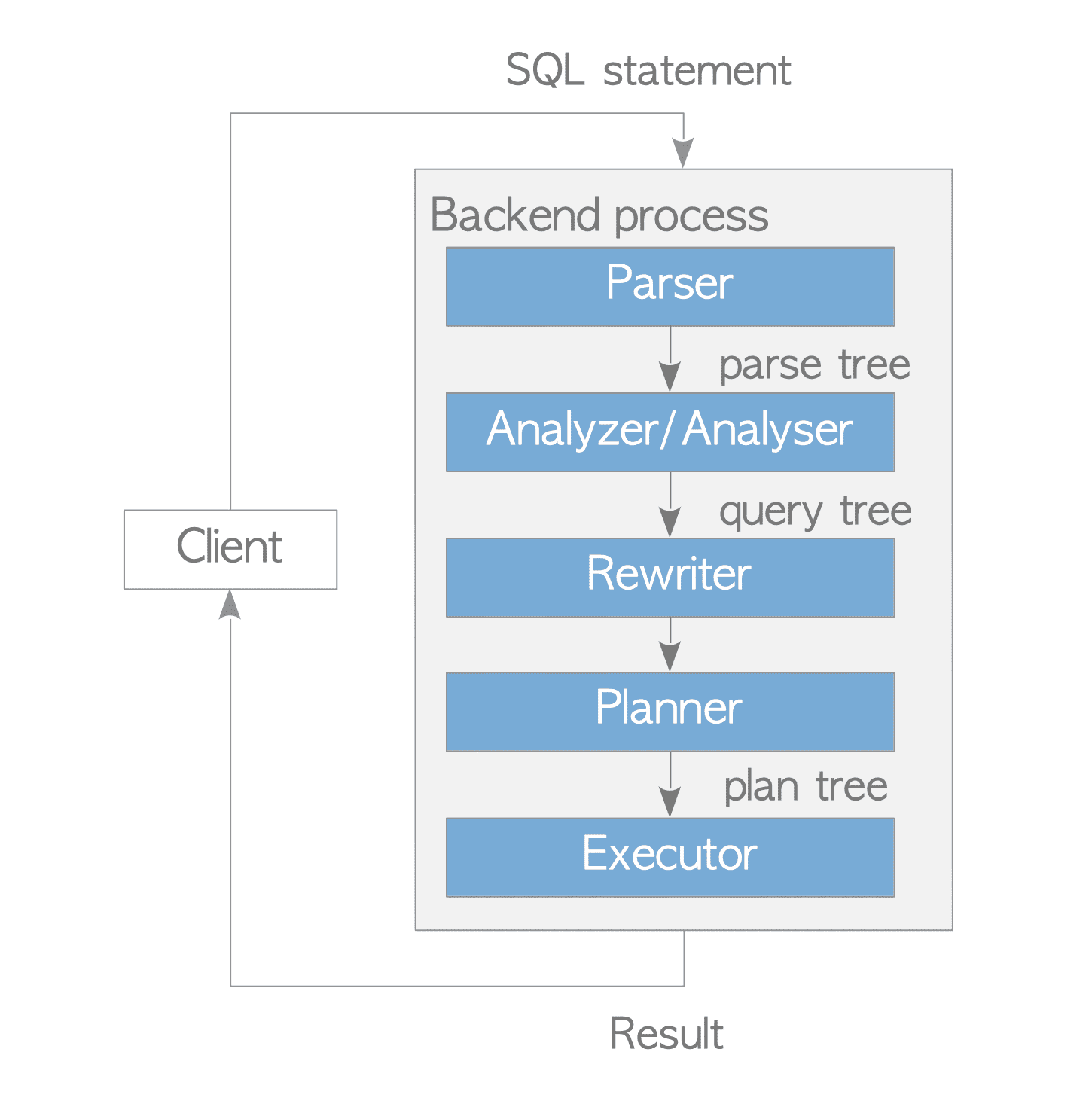
- PostgreSQL에서 Ver 9.6에 구현된 Parallel Query가 여러 Background Worker Process를 사용하나 Backend Process는 기본적으로 연결된 Client에서 실행되는 모든 Query를 처리함
- Parser: 일반 Text의 SQL문에서 Parse Tree(구문 분석 트리)를 생성
- Analyzer / Analyser: Parse Tree의 의미론적 분석을 수행하고 Query Tree를 생성
- Rewriter: Rule이 있는 경우 Rule System에 저장된 Rule을 사용해 Query Tree를 변환
- Planner: Query Tree에서 효율적으로 실행할 수 있는 Plan Tree를 생성
- Executor: Plan Tree에서 생성된 순서대로 Table과 Index에 Access해 Query 실행
Parser
- 일반 Text인 SQL문에서 후속 하위 System이 읽을 수 있는 Parse Tree 생성
SELECT id , data FROM tbl_a WHERE id < 300 ORDER BY data;- Parse Tree는 Root Node가 parsenodes.h에 정의된 SelectStmt 구조인 Tree
typedef struct SelectStmt { NodeTag type; /* * These fields are used only in "leaf" SelectStmts. */ List *distinctClause; /* NULL, list of DISTINCT ON exprs, or * lcons(NIL,NIL) for all (SELECT DISTINCT) */ IntoClause *intoClause; /* target for SELECT INTO */ List *targetList; /* the target list (of ResTarget) */ List *fromClause; /* the FROM clause */ Node *whereClause; /* WHERE qualification */ List *groupClause; /* GROUP BY clauses */ Node *havingClause; /* HAVING conditional-expression */ List *windowClause; /* WINDOW window_name AS (...), ... */ /* * In a "leaf" node representing a VALUES list, the above fields are all * null, and instead this field is set. Note that the elements of the * sublists are just expressions, without ResTarget decoration. Also note * that a list element can be DEFAULT (represented as a SetToDefault * node), regardless of the context of the VALUES list. It's up to parse * analysis to reject that where not valid. */ List *valuesLists; /* untransformed list of expression lists */ /* * These fields are used in both "leaf" SelectStmts and upper-level * SelectStmts. */ List *sortClause; /* sort clause (a list of SortBy's) */ Node *limitOffset; /* # of result tuples to skip */ Node *limitCount; /* # of result tuples to return */ List *lockingClause; /* FOR UPDATE (list of LockingClause's) */ WithClause *withClause; /* WITH clause */ /* * These fields are used only in upper-level SelectStmts. */ SetOperation op; /* type of set op */ bool all; /* ALL specified? */ struct SelectStmt *larg; /* left child */ struct SelectStmt *rarg; /* right child */ /* Eventually add fields for CORRESPONDING spec here */ } SelectStmt;
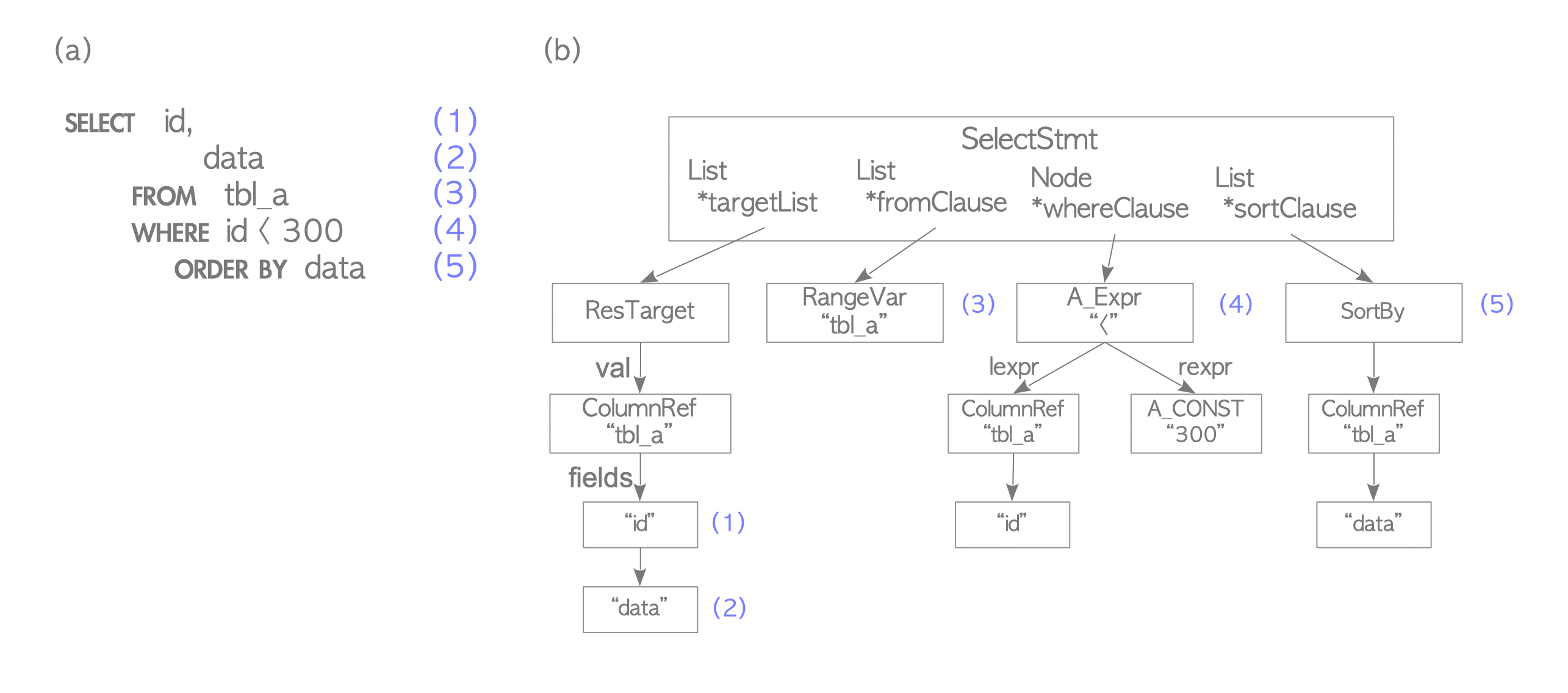
SELECTQuery의 요소와 Parse Tree의 해당 요소에 동일한 번호가 지정됨- ex) (1)은 첫 대상 목록의 항목 Table의
id열, (4)는WHERE절 등
- ex) (1)은 첫 대상 목록의 항목 Table의
- Parser는 Parse Tree를 생성할 때 입력의 구분만 확인하기에 Query에 Syntax Error가 있는 경우만 Error 반환
- Parser는 입력 Query의 의미를 확인하지 않음
- 의미 검사는 Analyzer가 수행
Analyzer / Analyser
- Parser에 의해 생성된 Parse Tree를 의미론적으로 분석 실행하고 Query Tree를 생성
- Query Tree의 Root는 parsenodes.h에 정의된 Query 구조
/* * Query - * Parse analysis turns all statements into a Query tree * for further processing by the rewriter and planner. * * Utility statements (i.e. non-optimizable statements) have the * utilityStmt field set, and the Query itself is mostly dummy. * DECLARE CURSOR is a special case: it is represented like a SELECT, * but the original DeclareCursorStmt is stored in utilityStmt. * * Planning converts a Query tree into a Plan tree headed by a PlannedStmt * node --- the Query structure is not used by the executor. */ typedef struct Query { NodeTag type; CmdType commandType; /* select|insert|update|delete|utility */ QuerySource querySource; /* where did I come from? */ uint32 queryId; /* query identifier (can be set by plugins) */ bool canSetTag; /* do I set the command result tag? */ Node *utilityStmt; /* non-null if this is DECLARE CURSOR or a non-optimizable statement */ int resultRelation; /* rtable index of target relation for INSERT/UPDATE/DELETE; 0 for SELECT */ bool hasAggs; /* has aggregates in tlist or havingQual */ bool hasWindowFuncs; /* has window functions in tlist */ bool hasSubLinks; /* has subquery SubLink */ bool hasDistinctOn; /* distinctClause is from DISTINCT ON */ bool hasRecursive; /* WITH RECURSIVE was specified */ bool hasModifyingCTE; /* has INSERT/UPDATE/DELETE in WITH */ bool hasForUpdate; /* FOR [KEY] UPDATE/SHARE was specified */ bool hasRowSecurity; /* row security applied? */ List *cteList; /* WITH list (of CommonTableExpr's) */ List *rtable; /* list of range table entries */ FromExpr *jointree; /* table join tree (FROM and WHERE clauses) */ List *targetList; /* target list (of TargetEntry) */ List *withCheckOptions; /* a list of WithCheckOption's */ OnConflictExpr *onConflict; /* ON CONFLICT DO [NOTHING | UPDATE] */ List *returningList; /* return-values list (of TargetEntry) */ List *groupClause; /* a list of SortGroupClause's */ List *groupingSets; /* a list of GroupingSet's if present */ Node *havingQual; /* qualifications applied to groups */ List *windowClause; /* a list of WindowClause's */ List *distinctClause; /* a list of SortGroupClause's */ List *sortClause; /* a list of SortGroupClause's */ Node *limitOffset; /* # of result tuples to skip (int8 expr) */ Node *limitCount; /* # of result tuples to return (int8 expr) */ List *rowMarks; /* a list of RowMarkClause's */ Node *setOperations; /* set-operation tree if this is top level of a UNION/INTERSECT/EXCEPT query */ List *constraintDeps; /* a list of pg_constraint OIDs that the query depends on to be semantically valid */ } Query;
- 이 구조는 명령의 유형(
SELECT,INSERT등) 및 여러 Leaf가 같은 해당 Query의 Metadata를 포함
- 각 Leaf는 목록 또는 Tree를 형성하고 개별 특정 절의 Data를 보유
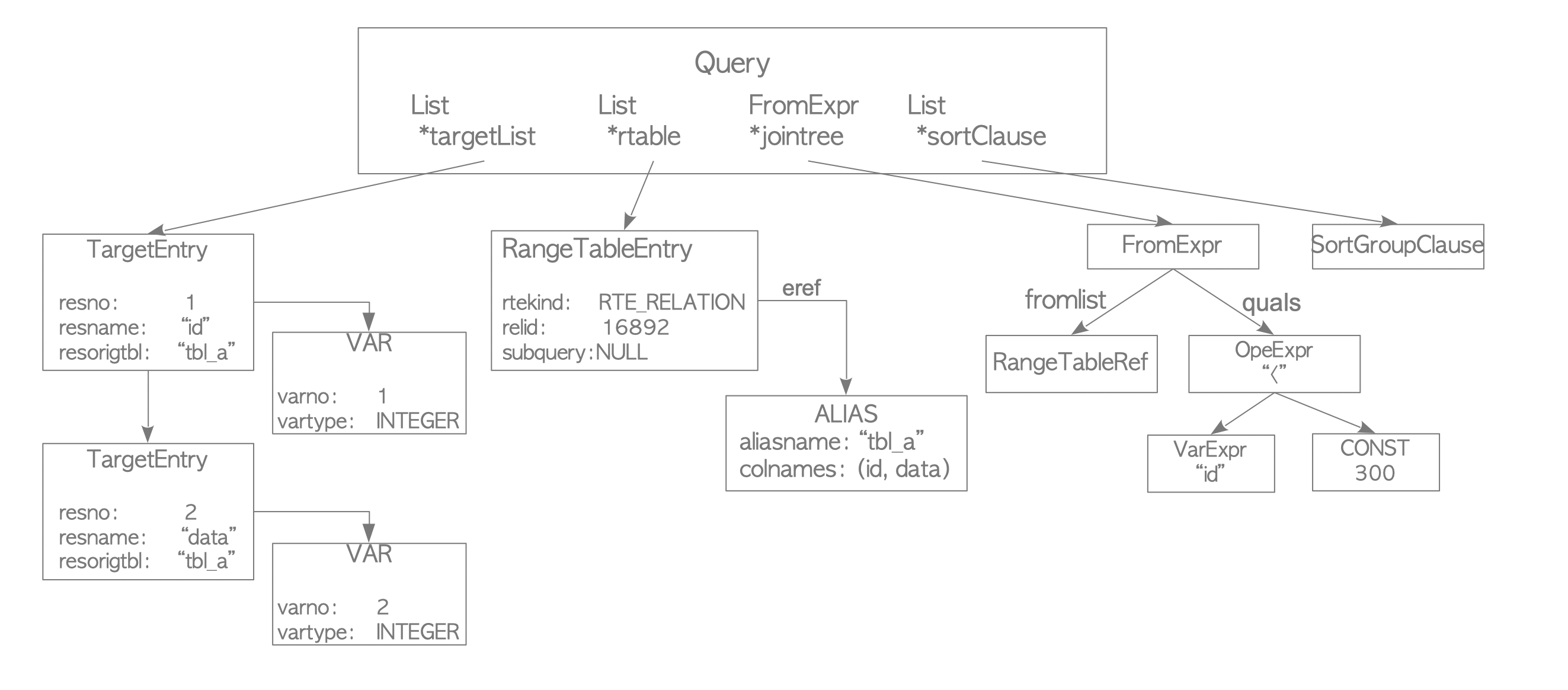
- TargetList: 이 Query의 결과인 Column 목록
- 예에서 Targetlist는
id,data로 구성
- 입력 Query Tree가
*인 경우 Analyzer는 명시적으로 모든 열로 대체
- 예에서 Targetlist는
- RangeTable: 이 Query에 사용되는 Relation 목록
- 예에서 이 Table은 Table의 OID 및 Table의 이름과 같은 Table
tbl_a의 정보를 가짐
- 예에서 이 Table은 Table의 OID 및 Table의 이름과 같은 Table
- JoinTree:
FROM절과WHERE절을 저장
- SortClause: SortGroupClause의 목록
Rewriter
- Rule System을 구현하는 System
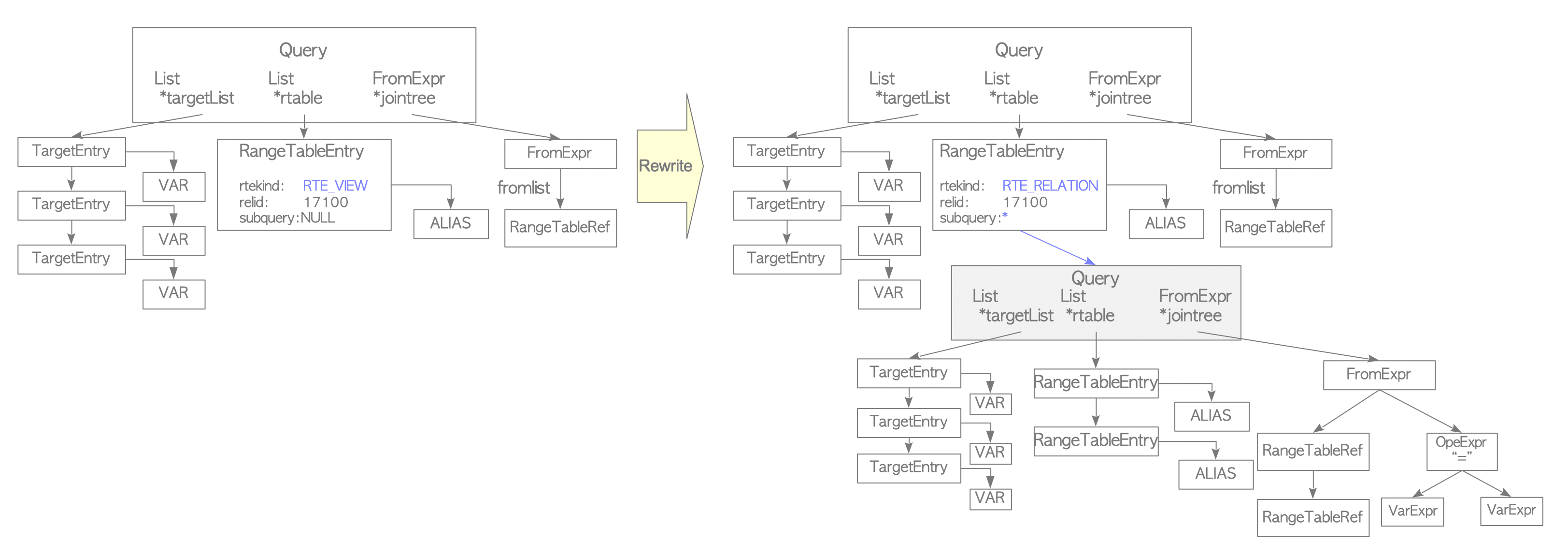
- PostgreSQL의 View는 Rule System을 사용해 구현됨
CREATE VIEWCommand로 View를 정의하면 해당 Rule이 자동으로 생성되어 Catalog에 저장됨
- ex)
CREATE VIEW employees_list AS SELECT e.id, e.name, d.name AS department FROM employees AS e, departments AS d WHERE e.department_id = d.id;SELECT * FROM employees_list;
Planner & Executor
- Planner는 Rewriter에게 Query Tree를 받아 Executor가 효율적으로 처리할 수 있는 (Query)Plan Tree를 생성
- PostgreSQL의 Planner는 비용 최적화를 기반으로 동작
- Rule 기반 최적화 및 Hint를 지원하지 않음(PPAS 지원)
EXPLAIN SELECT * FROM tbl_a WHERE id < 300 ORDER BY data;
QUERY PLAN
---------------------------------------------------------------
Sort (cost=182.34..183.09 rows=300 width=8)
Sort Key: data
-> Seq Scan on tbl_a (cost=0.00..170.00 rows=300 width=8)
Filter: (id < 300)
(4 rows)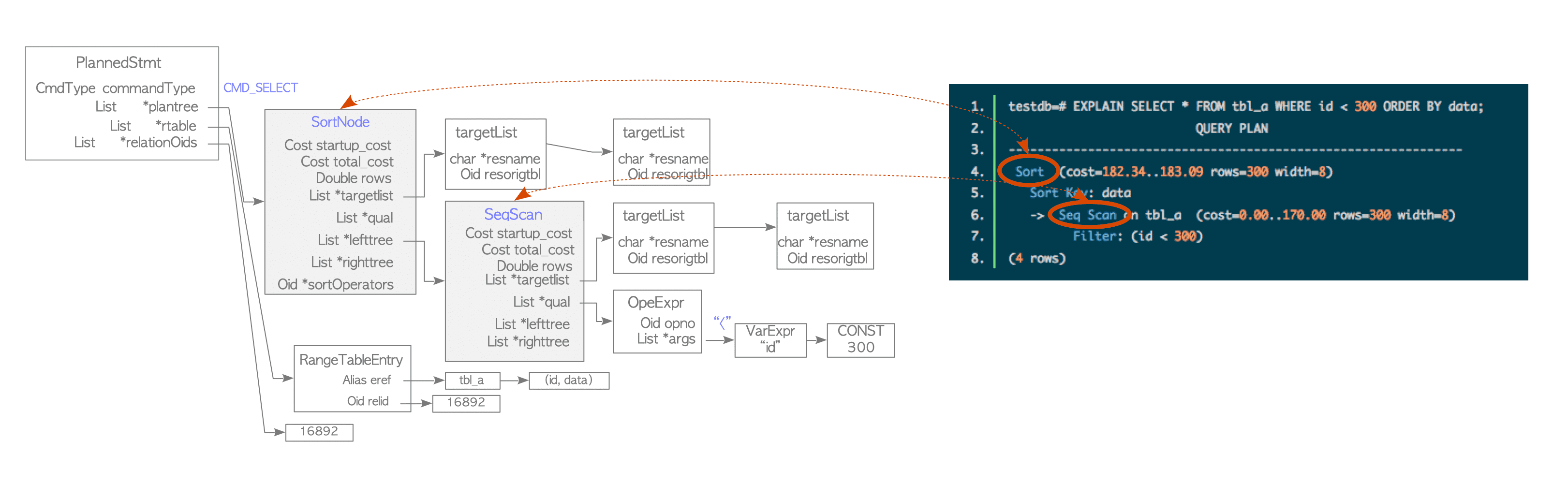
EXPLAIN Command 결과와의 관계- Plan Tree는 Plan Node라는 요소로 구성되며
PlannedStmt구조의 Plan Tree 목록과 연결
- 각 Plan Node에는 Executor가 처리에 필요한 정보가 있음
- Executor는 단일 Table Query의 경우 Plan Tree 끝에서 Root까지 처리
- 위 사진에서 표시된 Plan Tree는 Sort Node와 Sequential Scan Node의 목록
- Executor는
tbl_aTable을 Sequential Scan으로 Scan한 후 결과를 정렬
- Executor는
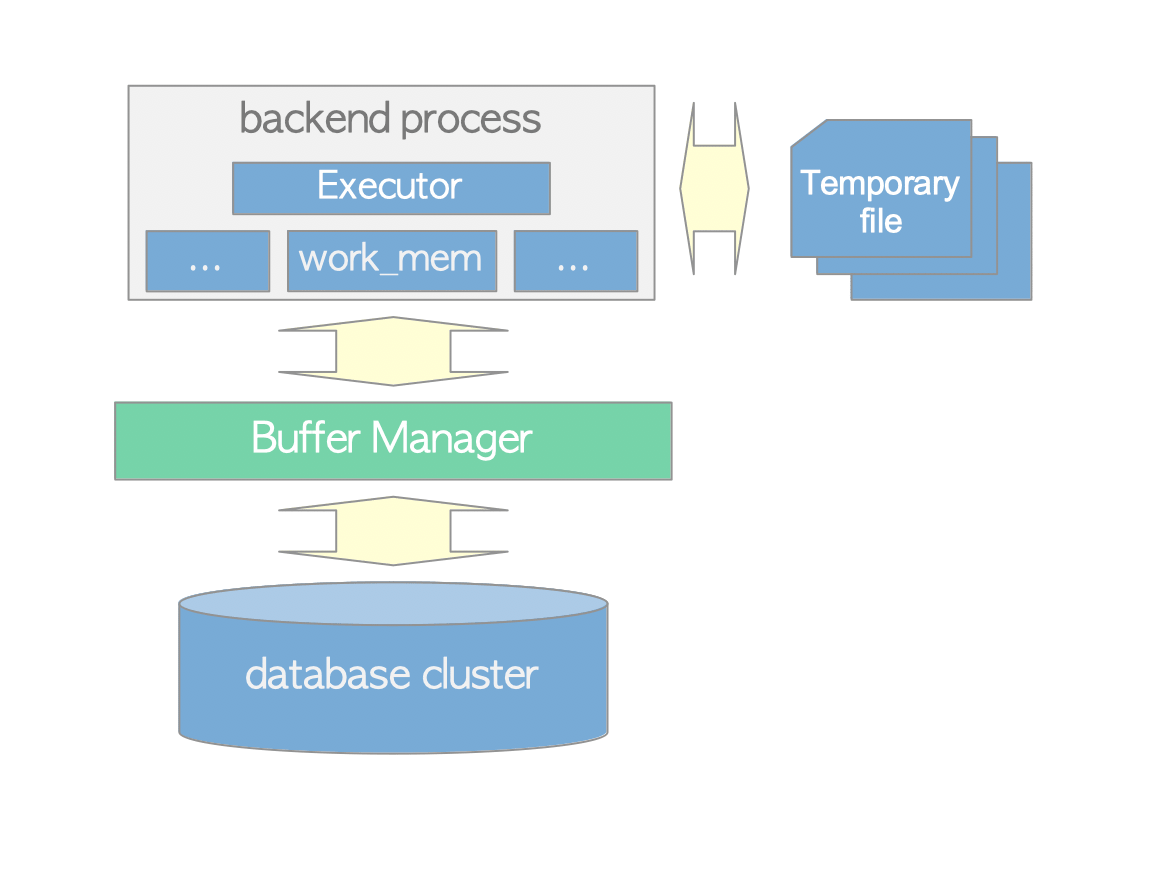
- Executor는 Buffer Manager를 통해 DB Cluster의 Table과 Index를 읽고 씀
- Executor는 Query를 처리할 때 미리 할당된
temp_buffers와work_mem같은 일부 Memory 영역을 사용하고 필요한 경우 Temporary File을 생성
- Row에 Access할 때 PostgreSQL은 CC 매커니즘을 사용해 실행중인 Tx의 일관성과 독립성을 유지
😮💨
Uploaded by N2T

 https://www.interdb.jp/pg/pgsql03.html
https://www.interdb.jp/pg/pgsql03.html


