Tuple(Row)를 작성하고 읽는 방법
Heap Tuple 작성
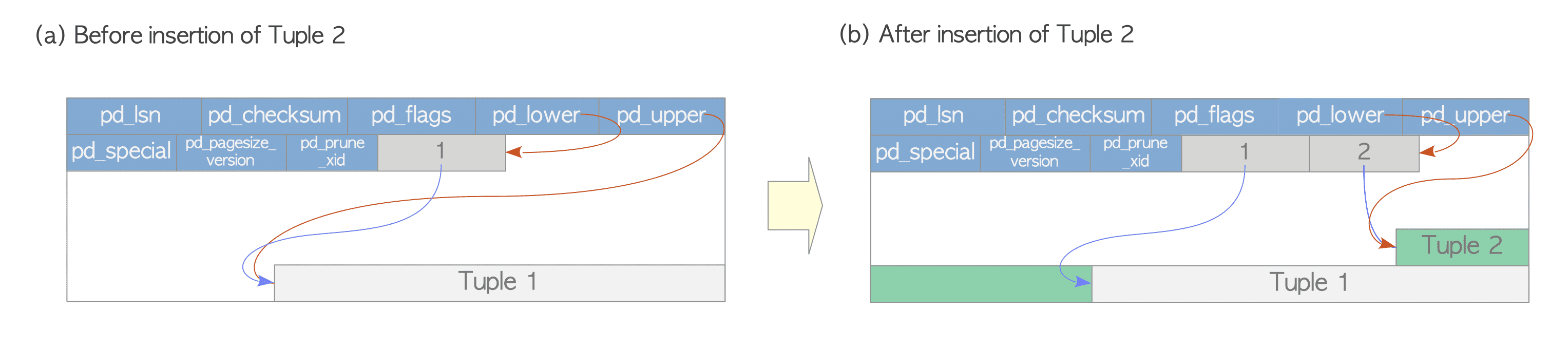
- 그림 (a): 하나의 Heap Tuple만 포함하는 하나의 Page로 구성된 Table을 가정했을 때 이 Page는
pd_lower는 첫 번째 Line Pointer를 가리킴 Line Pointer와pd_upper는 첫 번째 Heap Tuple을 가리킴
- 그림 (b): 두 번째 Tuple이
INSERT되며 첫 Tuple 다음에 배치됨 두 번째 LinePointer는 첫 Tuple 위로 Push되고 두 번째 Tuple을 가리킴pd_lower는 두 번째 Line Pointer를 가리키도록 변경되고pd_upper는 두 번째 Heap Tuple을 가리킴 이 Page 내의 다른 Header Data(pd_lsn,pg_checksum,pg_flag)도 적절한 값으로 다시 작성
Heap Tuple 읽기
- Access 방법은
Sequential Scan과B-tree Index Scan이 있음Sequential Scan: 각 Page의 모든 Line Pointer를 스캔 모든 Page의 모든 Row를 순차적으로 읽음
B-tree Index Scan: Index File에는 Index Tuple이 포함되어 있으며 각 Index Tuple은 대상 Heap Tuple을 가리키는 Key와 TID로 구성됨 찾고 있는 Key가 있는 Index Tuple이 발견되면 PostgreSQL은 찾은 TID값을 이용해 원하는 Heap Tuple을 읽음
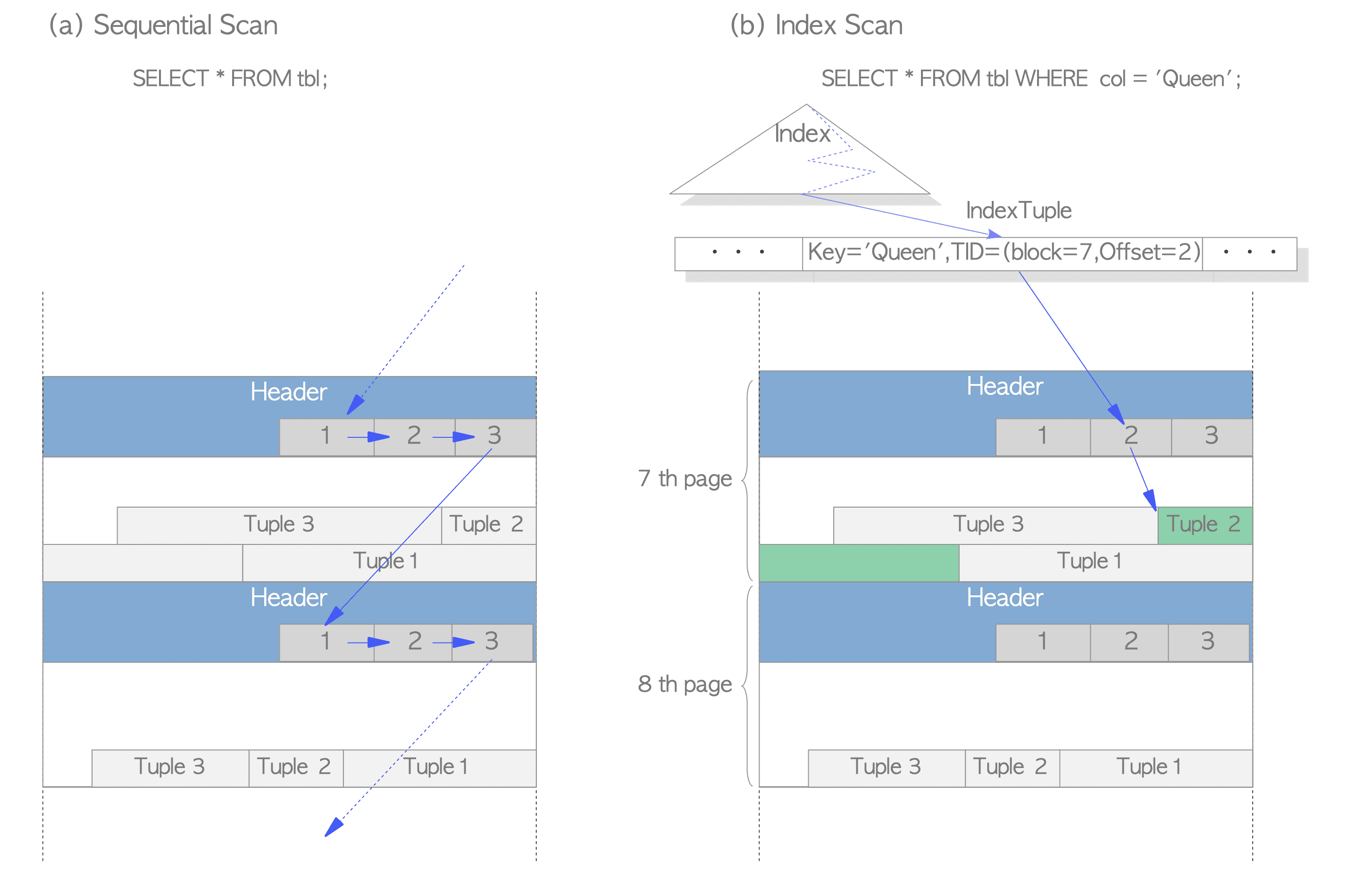
- 그림 (a): 순차적으로 모든 Row를 읽음
- 그림 (b): Index에서 획득한 TID값은 (Block=7, Offset=2)이므로 대상 Heap Tuple의 Table 내 7번째 Page의 2번째 Row임을 알 수 있음(불필요한 Scan 없이 원하는 Heap Tuple을 읽음)
ℹ️
PostgreSQL은 TID-Scan, Bitmap-Scan 및 Index-Only-Scan 지원
TID-Scan은 원하는 Tuple의 TID를 이용해 Tuple에 직접 접근하는 방식
SELECT ctid, data FRO< sampletbl WHERE ctid = '(0,1)';
ctid | data
-------+-----------
(0,1) | AAAAAAAAA
(1 row)Introduction
Hironobu SUZUKI I graduated from graduate school in information engineering (M.S. in Information Engineering), have worked for several companies as a software developer and technical manager/director. I published seven books in the fields of database and system integration (4 PostgreSQL books and 3 MySQL books).
 https://www.interdb.jp/pg/
https://www.interdb.jp/pg/
Uploaded by N2T



